In this article we are going to explain the four stages that make up the life cycle of a product, how you can identify which stage a product is in and which are the most appropriate marketing strategies for each of them.
In this way, you will be able to better understand the behavior of your product in the market and adapt your marketing strategies to each stage of the life cycle and obtain better results.
What is the life cycle of a product?
Have you ever wondered why some products become sales phenomena while others pass by without a trace? The answer lies in how a company manages each stage of each product’s life cycle .
The life cycle of a product is the natural process that a product goes through from its launching on the market until its eventual disappearance.
The 4 stages of a product’s life cycle
In general terms, it can be said that a product goes through 4 stages: introduction, growth, maturity and decline.
- Introduction
Introduction is the first stage of the product life cycle. During this stage, the product is launched on the market and attempts are made to capture the attention of the target audience, as consumers are not yet familiar with it and demand is low.
During this first phase, the price of the product is likely to be high due to production and distribution costs. Companies will need to invest in advertising and promotion to raise product awareness and generate consumer interest.
Read marketing strategies for the introduction stage
- Growth
During the growth stage, the product begins to gain popularity and experiences an increase in sales and profits. However, during this stage there is an increase in the number of competitors in the market. Therefore, it is a critical moment in which it is necessary to focus on promoting and improving the product in order to continue growing.
It is important to implement strategies to highlight the product and consolidate the brand image in the market.
Read marketing strategies for the growth stage
- Maturity
The maturity stage is the longest stage of the product life cycle and is characterized by a slowdown in sales growth.
During this period, demand begins to stabilize and competitors are well established. The price of the product may decrease further and companies will have to focus on maintaining customer loyalty and improving product quality to maintain their position in the market.
Read marketing strategies for the maturity stage
- Decline
The decline stage is the period when the product begins to lose popularity and sales. At this stage, demand decreases and the strongest competitors succeed in eliminating the product from the market. During this phase, important decisions must be made, such as whether to continue investing or to withdraw from the market.
Read marketing strategies for the decline stage
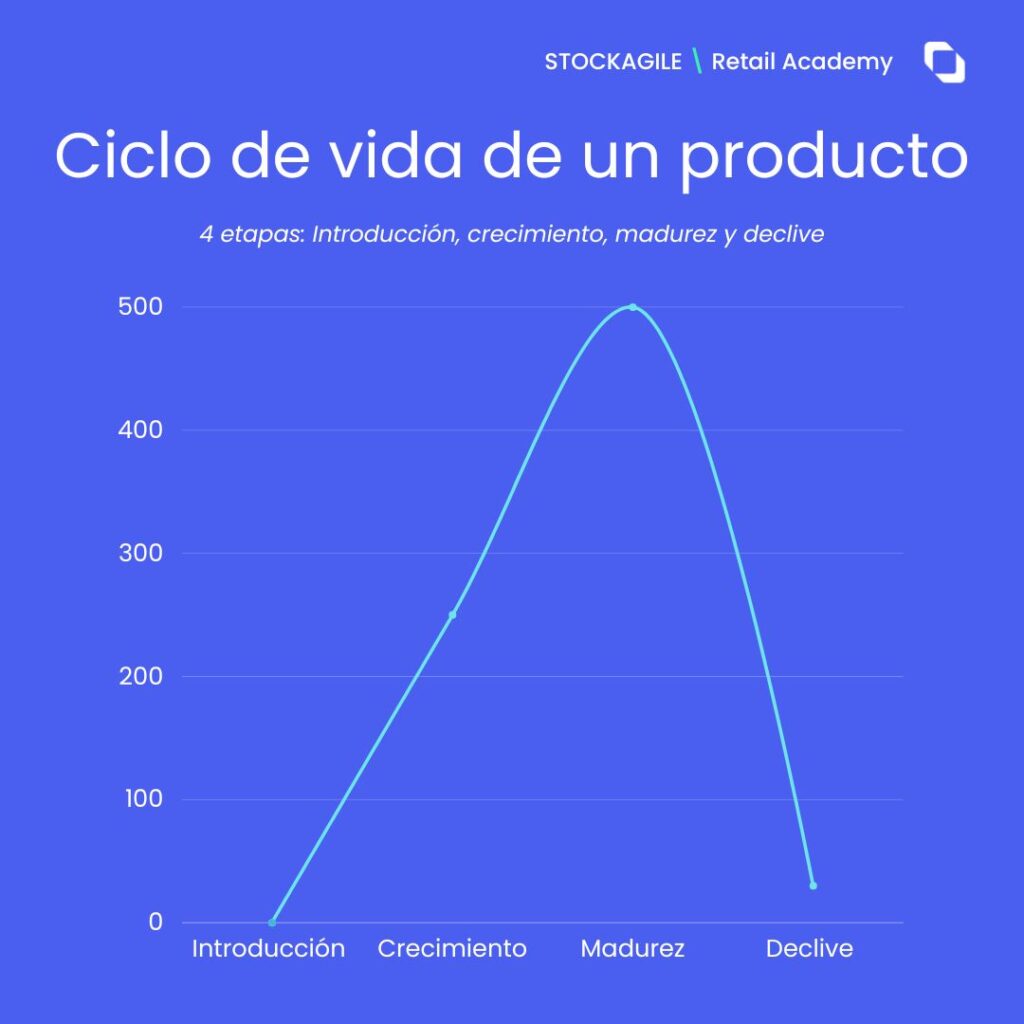
It is important to mention that not all products go through all stages of the life cycle. Some products may have a short life and never reach the mature stage, while others may have a long life and remain at the mature stage for many years.
In addition, it is possible for a product to return to the introduction or growth stage by implementing new marketing strategies, such as launching a new version of the product or expanding into new markets.
How to identify the stage of a product’s life cycle? 3 tips
Knowing what stage a product is in is important because it allows you to make better decisions about how you should approach your marketing and development strategies .
Otherwise, you could be missing out on growth opportunities or even jeopardizing the profitability of your business.
Here are 3 key tips to identify the stage of a product’s life cycle:
- Analyze the market situation. To this end, it is essential to assess whether there is a variability of changes in the industry in which the product is found, as this may limit its life cycle and favor the introduction of new and improved products.
- Evaluates consumer behavior. To know the degree of market approval, it is important to analyze whether the product is part of everyday consumer items, whether it solves common problems in consumers’ lives and whether its use is complex or simple.
- Study the competition: The ease of manufacturing products similar to yours can influence their success or failure and define their life cycle in the market. To do this, you will need to delimit the number of relevant competitors, their level of commercial expertise, pricing, distribution channels and other key points.
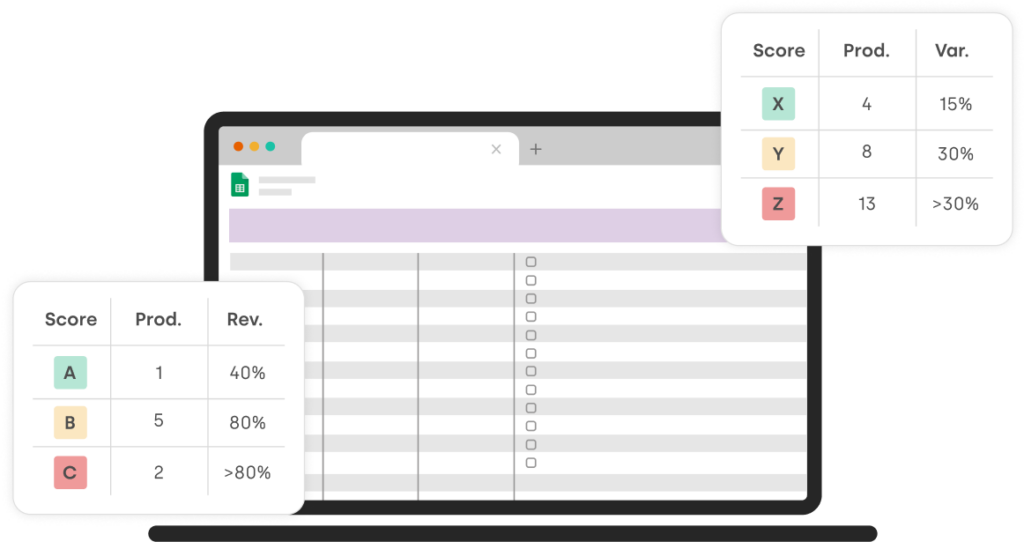
Identify and prioritize your most important products with our ABC XYZ classification template in Excel. Download it now and focus your efforts!
Marketing strategies for each stage of the product life cycle
Marketing strategies are critical to the success of a product throughout its life cycle. These techniques enable companies to identify their market needs and adapt their strategies accordingly.
During the product life cycle, marketing strategies can help increase product visibility and demand, build loyalty among existing customers and attract new consumers. In addition, these techniques allow the company to stay relevant in a constantly evolving market and to face competition effectively.
Here are some marketing strategies you can use at each stage of the product life cycle:

1. Marketing strategies during the introduction stage
During the introduction phase, it is important to create brand awareness and generate demand for the product. Some effective marketing strategies for this phase include:
- Promotions: Offering promotions, such as discounts or free samples, helps to attract customers and create an incentive to try the product.
- Demonstrations: Showing how the product works is a good way to attract the attention of potential customers and help them understand how the product can benefit them so that they decide to buy it.
- Influencer marketing: Using influencers on social networks is a good option to promote the product and create brand awareness. For example, a clothing brand may collaborate with a fashion influencer to show how to combine items in their store.
- Mass media advertising: Use television, radio and print advertising to reach a broad audience and create brand awareness. For example, a fast food brand may launch a TV commercial during a major sporting event to reach a large audience. This point will also depend on the company’s budget.
- Creating unique brand experiences: Create unique and emotional experiences that consumers associate with the brand. For example, a clothing brand can organize an event in which it invites its customers and offers different attractive activities. Once the event is over, you will be able to disseminate all photos and videos on social networks.
A successful example of a marketing strategy for this stage is the launch of Apple’s first iPhone in 2007. Apple implemented several strategies to raise awareness of the product, such as television advertising, limited release and promotion of exclusivity, which generated high consumer demand and established the iPhone as a high-end, exclusive product.

2. Marketing strategies during the growth stage
During the growth phase, the objective is to increase market share and build a loyal customer base. Some effective marketing strategies for this phase include:
- Product customization: Offer customization options to meet specific consumer needs and desires. For example, an athletic footwear brand may offer online customization options for consumers to design their own sneakers.
- Exceptional customer service: Deliver exceptional customer service to build customer loyalty and increase brand loyalty. For example, an electronics brand may offer free technical support and an extended warranty for its products.
- Market expansion: Identify new market segments or expand geographically to increase market share. For example, a coffee brand may expand into new international markets to increase its global presence.
An example of a textile brand that has experienced a successful growth phase is Zara, the Spanish fashion retailer. During the 1990s and 2000s, Zara rapidly expanded internationally, opening stores around the world and increasing its online presence.

The brand has been successful in implementing differentiation strategies, such as the production of small quantities of clothing with exclusive designs, which has helped to create a sense of exclusivity and novelty among consumers.
In addition, its “fast fashion” business model has allowed it to quickly adapt to the latest fashion trends and offer new collections in a short period of time.
3. Marketing strategies during the maturity stage.
During the maturity stage, the objective is to maintain market share and generate consistent profits. Some effective marketing strategies for this phase include:
- Product diversification: Introducing new products or services to meet changing consumer needs and desires and to attract new market segments. In the case of a fashion store, you can add new lines in your stores, such as: maternity, teenager and plus sizes, (in case you do not already include them).
- Cross-selling: The company can offer complementary or related products to encourage customers to buy more. For example, a camera brand may offer discounts on camera accessories when purchasing a new camera.
- Continuous innovation: Constantly improve existing products or services to keep up with market trends and expectations. For example, a technology brand may regularly update its software and hardware to improve performance and user experience.
- Value-based content marketing: Emphasize the benefits and value of products or services to maintain the loyalty of existing customers and attract new customers. For example, a personal care brand can highlight the natural ingredients and quality of its products in its marketing campaign or write articles of interest to its target audience in a blog on its website.
- Cost-based competition: Reduce production costs and prices of products or services to remain competitive in the market. For example, a clothing brand can reduce production costs by using cheaper materials or outsourcing production to other countries.
During the maturity stage, Kellogg’s implemented several marketing strategies to maintain its position in the breakfast cereal market. The brand launched an advertising campaign comparing its product with that of its competitors, highlighting the superior quality and taste of Kellogg’s cereals.
It also focused on product innovation to meet customer demands, launching new products such as organic and gluten-free cereals.
Finally, the brand also offered cross-selling promotions to encourage customers to buy more products, such as discounts on cereal bars and dried fruit when buying a pack of cereals.

These marketing strategies were effective in maintaining Kellogg’s as a leading brand in its category, despite increasing competition in the marketplace.
4. Marketing strategies during the decline stage.
During the decline stage, the objective is to maintain profitability and minimize losses. Some effective marketing strategies for this phase include:
- Exit strategies: Identify opportunities to profitably exit the market, such as the sale of assets or the orderly liquidation of inventory.
- Cost reduction and discounting: Reduce production prices and overhead to increase profitability. For example, a brand can reduce costs by switching to cheaper materials and eliminating products that are not selling well. Another option is to offer discounts to get products to sell.
- Focus on the niche market: Concentrate on a smaller, profitable niche market, rather than trying to compete in a larger, saturated market. For example, a cleaning products brand may focus on pool cleaning or boat cleaning.
- Brand repositioning: Changing the brand image and marketing strategy to attract new market segments or to improve brand perception in the current market. For example, a motorcycle brand may shift its focus from speed and excitement to safety and reliability.
- Reducing marketing spend: Reduce advertising and promotional spending to maximize profitability and minimize losses. For example, a brand can reduce spending on traditional advertising and focus on low-cost or organic digital marketing.
During the 1990s, Kodak faced increasing competition from digital cameras. As technology advanced, demand for traditional cameras declined, leading Kodak into the decline stage.
To adapt to this situation, the company implemented several marketing strategies, including reducing prices, diversifying into digital photo printing and selling patents for additional revenue.

Despite these strategies, Kodak eventually filed for bankruptcy in 2012. However, this is a good example that shows how marketing strategies can help companies to face the decline stage and stay in the market, even if they are not always enough to save the company.
Optimize your product lifecycle management with Stockagile.
With Stockagile you will be able to keep track of your product inventory and update it in real time, which will allow you to have a clear view of its performance in the market. In addition, you can rely on data analysis and management tools to help you make informed decisions at every stage of the product lifecycle.
In the phase of product introduction to the market, our software will allow you to establish an appropriate pricing strategy and manage customer orders.
In the growth phase, it will help you manage inventory and plan production according to demand.
In the maturity phase, you will be able to analyze the sales data and adjust the marketing strategy to keep the product relevant in the market.
And finally, in the decline phase, you will be able to manage your inventory efficiently and make informed decisions on whether to retire or discount your product.





