Demand planning is a key tool for business decision making, as it allows you to anticipate your customers’ needs and improve their satisfaction while optimizing your production processes and stock flows.
In this article, we explain everything you need to know about demand forecasting, from the basics to more advanced methods, the tools that can help you and the common mistakes to avoid.
Factors to consider in demand forecasting
To make an accurate demand forecast, it is necessary to take into account several factors that may alter demand. Some will depend mostly on you and the way you manage your business and others will be given to you.
Here are some of the main factors to consider:
- Internal factors: Internal factors that may affect demand include the availability of products or services, their quality, prices and promotions offered, as well as the quality of customer service.
- External factors: These include economic factors, such as market conditions, consumer income levels and unemployment rates; social factors, such as culture, fashion and trends; and political factors, such as laws and regulations.

Demand forecasting methods
Demand forecasting methods can be divided into two main categories: quantitative methods and qualitative methods.
Quantitative demand forecasting methods:
Quantitative methods allow objective and accurate analysis based on numerical and statistical data, which is useful for forecasting numerical trends and making long-term projections in various fields, such as economics and finance. However, it is important to keep in mind that these methods may be limited in their ability to consider subjective or unpredictable factors that may influence the final results. Therefore, it is necessary to complement quantitative methods with other more subjective approaches, such as qualitative research and practical experience.
For example: a restaurant uses quantitative methods to predict the number of customers it will have on a given day. However, they do not take into account subjective factors such as weather, competition in the area, or the popularity of a new dish on the menu. If there is a rainy day or a popular new restaurant opens in the same area, demand could be much lower than they predicted and they could end up with excess food that doesn’t sell. This shows the limitation of quantitative methods in not considering subjective factors that may influence demand.
The main quantitative demand planning methods are:
- Trend analysis:
This method is based on the assumption that future demand will follow a linear, exponential or logarithmic trend based on historical data. The data are fitted to a trend line and used to project future demand. For example, if a company wants to forecast demand for a product for the next 6 months, it can use historical sales data for the last 12 months and fit a trend line to predict future demand. If this method is used, it is important to take into account seasonality factors that can create upward or downward patterns within a general trend. It is also important to bear in mind that in certain sectors, “fashions” have a major impact and that certain trends can be radically interrupted by the appearance of a new “fashion”.

- Statistical models:
One of the most widely used statistical models in demand forecasting is the moving average, which uses the average of a given number of previous periods to predict future demand. For example, if a three-month moving average is used, the average of the last three months’ sales will be taken to forecast next month’s demand. This model is useful for predicting short-term demand and adjusting inventory levels accordingly.
Another common statistical model is time series analysis, which is used to analyze seasonal, cyclical and trend patterns in historical data and project them into the future. This model is useful for forecasting long-term demand and for planning production and inventory levels accordingly.
- Analysis of historical data:
This method uses historical sales data and other economic indicators to project future demand. For example, if a company wants to forecast demand for a particular product, it can use historical sales data for that product, as well as relevant economic indicators, such as GDP or the consumer price index (CPI), to forecast future demand.
- Time series analysis:
This analysis is based on historical sales data. The data is analyzed to find seasonal patterns and long-term trends, and then statistical models are used to forecast future demand. This method is very useful for forecasting demand for products that have seasonal sales patterns, such as products for the Christmas season.
- Regression models:
The regression model uses historical sales data and other external factors to forecast future demand. External factors may include changes in the economy, competition and market trends. Statistical models are used to analyze the data and forecast future demand. For example, a beverage company may use a regression model to forecast the demand it will have based on the economy, health trends and changes in competition.
- Social network data analysis:
This method involves analyzing data from social networks. Data may include product or brand mentions on social media, customer comments and market trends on social media. For example, a fashion company can use this type of analysis to forecast future demand for a new clothing line based on current trends in social networks.
One example of success is SHEIN, the fashion platform that has revolutionized the retail world by implementing a fast fashion production model based on the analysis of trends in social networks. SHEIN uses social media data analysis to forecast future trends in fashion and adapt its production in real time, making it the platform par excellence for “real time retail”. For example, if a fashion trend begins to gain popularity on social media, SHEIN can respond quickly by producing and selling garments that fit that trend.

Qualitative demand forecasting methods:
The main advantage of qualitative methods is the ability to obtain detailed and in-depth information about consumers and their needs. These methods allow greater flexibility and adaptability to changing market situations, and can also be useful in the development of new products and services. However, their main drawback is that they can be subjective and do not provide an accurate quantitative measure of demand. Some examples:
- Opinion polls:
This method involves conducting surveys to obtain information on the opinions and expectations of consumers and experts. For example, a food company may conduct a survey to find out consumer preferences for flavors or the appearance of packaging.
- Delphi analysis:
The Delphi method involves bringing together a group of experts with a mediator and structured techniques to discuss and reach consensus on expectations of future demand.
The process is conducted anonymously to avoid influencing opinion and is used as a method of prospecting and analyzing future scenarios in order to make informed decisions and adopt the best strategies for the company.
3. Scenario analysis:
This is a technique in which different possible future scenarios are considered and demand is estimated for each of them. For example, a company may consider several possible scenarios in the economy and estimate demand in each of them, and then make decisions based on the results.
Common mistakes in demand forecasting to avoid
Making mistakes in forecasting demand can lead you to accumulate unnecessary stock or suffer the dreaded stock-outs .
Here are some of the most common mistakes that are often made when trying to plan for demand:
- Planning without sufficient historical data:
Suppose a clothing store has decided to add a new line of sportswear. However, the retailer has no historical data on sportswear sales, making it difficult to forecast demand for this new line. In this case, the store could collect market information, conduct surveys and seek competitor data to get a clearer picture of potential demand.It is important not to jump to conclusions based on too small a sample of data or extrapolate based on realities that do not fit our own.
- Failure to consider seasonality
A toy store can expect a significant increase in demand during the holiday season. If the store does not take seasonality into account, it could inadequately plan its production and inventory management. To avoid this, the store should consider seasonality when planning production and inventory management to ensure that it has sufficient stock during periods of high demand.It is vital to reverse engineer the onset of these high-demand periods and the timing of production and shipments to plan your orders and stock sufficient stock.
- Making decisions based on assumption or intuition:
Suppose an electronics retailer assumes that the demand for flat screen televisions will decrease due to the introduction of new technologies. However, demand for flat-panel TVs remains high due to their relatively low cost compared to the latest additions in the industry. If the store relies on this assumption, it could inadequately plan its orders and accumulate stock of a type of product with no demand and fall short of those products that its customers do order, leading to the worst situation of all: overstocking and stock-outs at the same time.
- Lack of communication between departments:
A clothing store might plan a sale in its winter clothing section to liquidate remaining inventory, but if the buying department is not aware of this sale, they might interpret it as a peak in demand and decide to continue buying more stock of that same collection, resulting in excess inventory and a financial loss for the store. To avoid this, it is important that departments work together and share relevant information for accurate and consistent forecasting.

Download the demand planning ebook now! Learn the keys to optimize the availability of your products and provide a better service to your customers.

How to improve the accuracy of your demand forecasts?
Although forecasting demand is never an easy task, there are a number of strategies that can help companies improve the accuracy of their forecasts and reduce the risks associated with inventory management and production planning. In this section, we’re going to show you some of the most effective ways companies can improve demand forecasting accuracy and ensure their operations are always one step ahead.
- Improved data quality:
Digitized stock management is the first step to ensure that you have accurate turnover data. Inventory on a frequent basis and record inter-store transfers, theft, losses and discounts.
Having tools such as a people meter can also be useful to understand not only the sales of your stores, but also their traffic and the conversion of visitors to sales of your sales team.
- Integration of data from different sources:
For example, an electronics retailer wants to improve the accuracy of its product demand forecasting. To do so, it could combine internal data, such as sales history and production data, with external data, such as market trends and consumer behavior. By integrating this data, the business could gain a more complete view of demand and improve forecasting accuracy.
- Continuous monitoring and adjustment of demand forecasting: Suppose a sporting goods store wants to improve the accuracy of demand forecasting for seasonal products, such as swimsuits in summer and coats in winter. To do so, you could use analytical tools and techniques to monitor deviations from the actual forecast and adjust accordingly. By doing so, the store could improve forecast accuracy over time and keep market demand as accurate as possible.
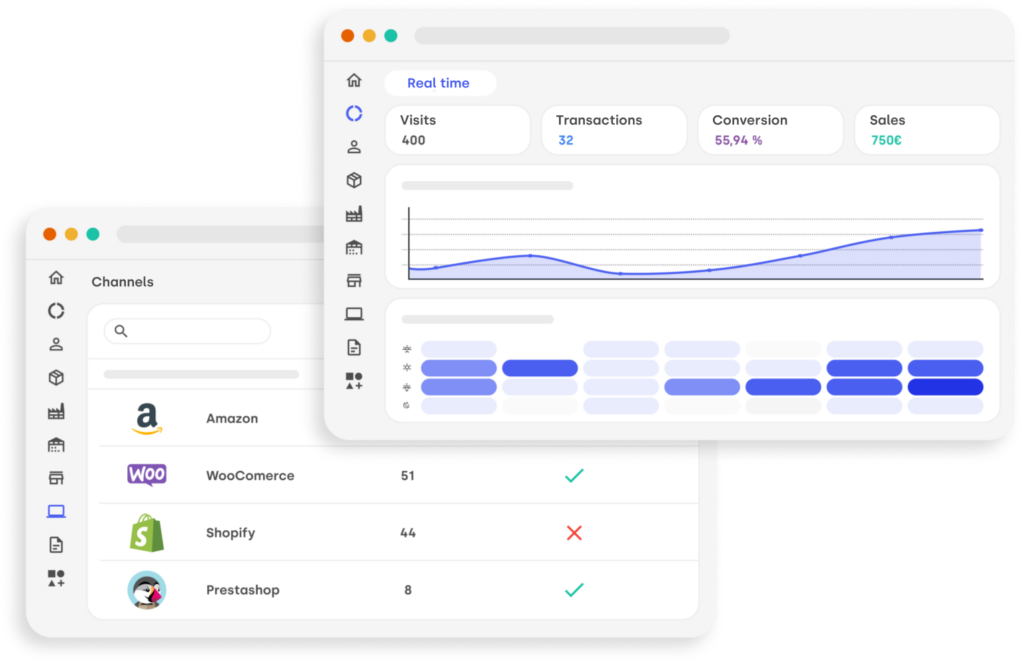
Find out how Stockagile can help you forecast your demand
Stockagile uses analytics and machine learning techniques to generate accurate demand forecasts and provides real-time information on sales performance and inventory levels.
In addition, Stockagile allows you to continually adjust and refine forecasts as more data is collected and new sales are made, which can help ensure that inventory levels are optimized and products are available to customers when they need them.
Finally, having a software like Stockagile will help you to adapt your purchasing and replenishment strategy to this demand, improving the efficiency of your business.

In conclusion, demand forecasting is a crucial task for any business that wants to optimize its supply chain and maximize its profitability. With so many factors that can affect demand, it is important for companies to use a combination of quantitative and qualitative methods to more accurately forecast future trends.
At the same time, it is important for companies to be on the lookout for common forecasting mistakes and to work on continuously improving data quality and monitoring their business to adjust their forecasts accordingly.