Barcodes are an essential tool in trade and logistics. There are several types, each with its own characteristics and uses. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the main types of barcodes and help you choose the right one for your needs.
What is a barcode?
A barcode is a graphical representation of numeric or alphanumeric information that is read by a scanner. Barcodes facilitate the tracking and identification of products, as well as the automation of processes in different sectors.
Main types of barcodes
There are two general categories of barcodes: linear and two-dimensional (2D). Below, we will examine the most common types within each category.

Linear barcodes (1D):
EAN (European Article Number) bar code:
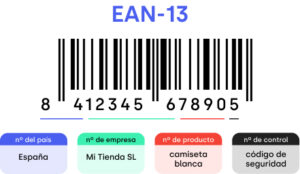
It is one of the most widely used codes in Europe. It is frequently used in supermarkets where the registration process is usually very fast. These codes generate fewer reading errors than other alternatives. The European Article Number (EAN) or GTIN (Global Trade Item Number) is usually printed on the product packaging and encoded as a bar code.
It consists of the country code, manufacturer code, product code and a check digit.
There are two versions (one long and one short):
- EAN-13 (13 digits): This is the standard version of EAN.
- EAN-8 (8 digits): Usually used for small products.
The standard barcode can be enlarged or reduced within the resizing range of 0.8 to 2.0. The range for narrow bar width is 0.26 to 0.66 mm 0.010″ to 0.026″.
There is a somewhat peculiar type of EAN code that is commonly used for books:
- ISBN: The barcode is formed with the classification code (classified by subject of sale, origin of publication, content) and the price code (excluding taxes) which is combined with the ISBN.
UPC (Universal Product Code) bar code:
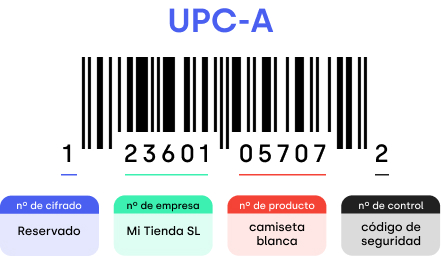
Widely used in the retail trade, especially in North America. EAN in Europe and JAN in Japan are based on the UPC.
The UPC-A is only used in the USA. and Canada and does not carry a country code. In turn, the first digit, called the number system (NS) character, defines the content of the information.
There are also two versions:
- UPC-A or UPC-12 (standard 12-digit version)
- UPC-E ( 6-digit reduced version )
ITF (Interleaved Two of Five)
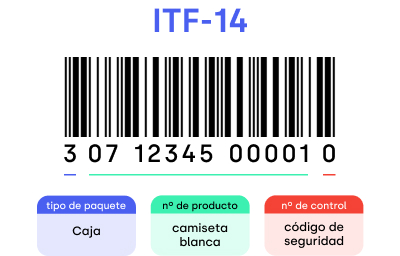
It is widely used as the standard distribution code printed on corrugated boxes. There are several types called “2 of 5” as shown below. All of them represent a
character, using the same composition consisting of 2 wide bars (spaces) out of 5 bars (spaces). Although their composition is similar, the code is completely different:
- Interleaved “2 of 5” (ITF): This is the standard version of this family of codes.
- Industrial “2 of 5”: In the past, this code was used in industrial applications. As this code assigns information only to bars, not spaces, the code size increases. It is not currently used in many areas, except for distribution management.
- Matrix “2 of 5”: This code is different from the industrial “2 of 5”, because both bars and spaces contain information.
- COOP “2 of 5”: This code is used in a consumer cooperative organization (coop) and is called a COOP code.
- IATA: This code is used for air cargo management by IATA (International Air Transport Association).
As ITF is a barcode with a very high data density, it offers the following features:
- The size of the label may be smaller than other codes with the same digits.
It is effective for printing barcodes in small spaces. - It can contain more data compared to other codes, at the same label size. (The number of digits can be increased)
- A wider bar width is possible, if the size of the label and the number of digits are the same. The wider the bars are, the easier it is for the barcode reader to read them. It is also possible to read at a greater distance.
- While ITF has many advantages, it also has the disadvantage of a possible “reading omission” due to its
composition.
CODE 39
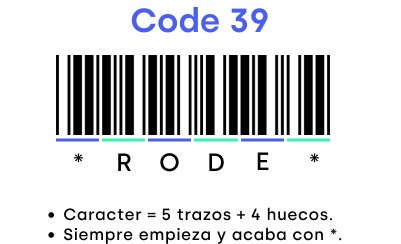
Code 39 is one of the oldest alphanumeric barcodes used in various industries. The greatest advantage of this code is the great variety of characters and combinations it offers. It supports numeric values, letters of the alphabet and even symbols (comma, period, space, $, /, +, %). The main drawback is that it has a low tolerance and low information density.
Codabar
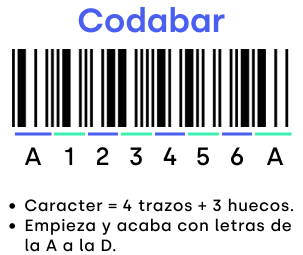
Codabar is a numeric code with 6 additional special characters (0..9 as well as – : / . . +). Each codabar character is represented by 7 elements (4 strokes, 3 gaps). The information density of this code is quite low.
It is widely used for applications requiring serial numbers, such as for blood bank management, receipts for door-to-door delivery services and membership cards.
CODE 128
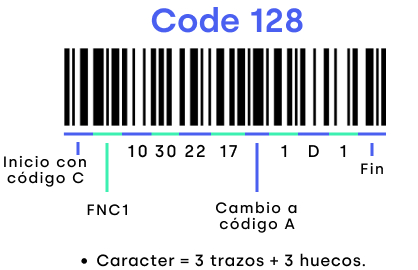
Code 128 is a highly versatile code type capable of encoding all ASCII characters. It is commonly used in logistics and transportation.
Since it can represent all characters (except Japanese kanji, hiragana and katakana) that can be worked with a computer keyboard, it is a computer-friendly barcode.
Since CODE 128 uses 4 types of bar size, printers with high print quality are required. CODE 128 is not suitable for printing with dot matrix or FA inkjet printers, nor for flexographic printing on corrugated board.
Two-dimensional (2D) barcodes
QR Code (Quick Response)

It is very popular in marketing, advertising and mobile applications, as it can store large amounts of information and links to websites. Most modern smartphones come equipped with the ability to scan these codes with the device’s camera making it very accessible to the consumer.
Data Matrix

It is a type of code widely used in manufacturing and logistics, especially for labeling electronic components and pharmaceutical products. It can contain a large amount of data in a small space.
Unlike linear barcodes, such as the UPC or EAN barcode, a Data Matrix code has a two-dimensional structure. This means that it can store information in both the horizontal and vertical directions.
It consists of 4 main components:
- Data area: The area containing all the encoded information.
- Fixed boundary line: The corner represented by an unbroken line in the normal alignment to the left and to the bottom of the data area. This is used to detect the code and its location during analysis.
- Open boundary line: This is the opposite corner of the “fixed boundary line”. These lines (above and right) consist alternately of black and white dots, so they are open lines. They are used to determine rows and columns during analysis.
- Rest area: This is the area surrounding the code. This interval must be at least as wide as one column/row or one point in the code.
The size of a Data Matrix code can vary depending on the amount of information to be stored. It can have from a few cells to thousands of cells. The most common size is between 10×10 and 144×144 cells.
Due to their two-dimensional structure, Data Matrix codes can store a larger amount of information compared to linear barcodes. The amount of information it can store depends on the size of the code and the type of data being encoded.
Data Matrix codes often incorporate error correction techniques to ensure reading accuracy, even if parts of the code are damaged or unreadable. This makes Data Matrix codes more robust and reliable.
Despite their ability to store a large amount of information, Data Matrix codes take up relatively little physical space. This makes them ideal for printing on labels, packaging or small surfaces.
PDF417

designed to store large amounts of data, including text, numbers and binary files. Common on ID cards, such as driver’s licenses and passports.
PDF417 codes do not have a fixed predefined length. They can be adapted to different data lengths, as they can expand or contract as required. In addition, the data density can be adjusted to optimize readability and the space occupied by the code.
PDF417 codes are used in a wide variety of applications, such as package shipping and tracking, transportation tickets, ID cards, inventory management and mobile payment systems.
Aztec

Aztec codes are another type of two-dimensional barcode used to store information in the form of dot and bar patterns.
They have a compact structure that allows them to occupy less physical space compared to other two-dimensional barcodes. This makes them suitable for applications where space is limited.
Aztec codes are composed of a series of concentric rings around a central point. These rings contain the encoded information in the form of dot and bar patterns. The number of rings and the density of the information can vary according to the coding needs.
These codes are designed to be error and damage resistant. They incorporate error correction techniques that allow the code to be readable even if parts of it are damaged. This improves reading reliability and resistance to adverse conditions.
Easily create barcodes for your products and optimize your inventory with Stockagile.
How to choose the right barcode for your needs?
When selecting a barcode, consider the following factors:
- Type of information: consider what type of data you want to store (numeric, alphanumeric, binary) and the amount of information.
- Compatibility: make sure that the barcode is compatible with the scanners and systems used in your industry or region.
- Size and space: some barcodes require more space than others. Choose a type that suits the size of your labels and products.
- Resistance: In harsh environments, such as logistics and manufacturing, you may need barcodes that are more resistant to dirt and wear.
- Industry standards: research your industry standards and regulations before deciding which barcode to use.
Conclusion
Barcodes are essential for trade, logistics and product identification. There are numerous types of barcodes, each with its own characteristics and applications. When choosing the right barcode, consider factors such as type of information, compatibility, size and your industry regulations. We hope this guide has provided you with valuable information to make an informed decision.





